Test Amit sep
How to deal with Diabetes: Effective management and Medications
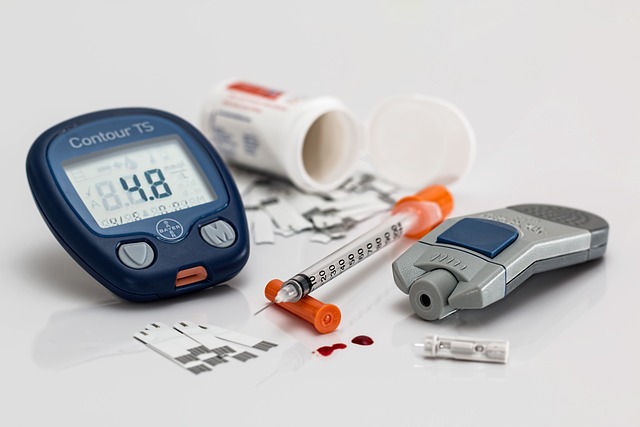
To manage diabetes, there are several things you can do:
Maintain a healthy diet by following a balanced meal plan and limiting sugary and processed foods.
- Regular physical activity helps regulate blood sugar levels and maintain a healthy weight.
- Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, as prescribed by your doctor.
- Taking medication as prescribed and on time.
- Quitting smoking if you smoke.
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, or counseling.
- Regular visits to your doctor and eye doctor to check for complications.
The estimated population with diabetes worldwide was around 463 million. This number is projected to increase to 700 million by 2045. Diabetes is a leading cause of death and disability and is associated with a range of health problems, and nerve damage, including heart disease, and kidney disease. Effective management of diabetes can help prevent or delay the development of these and other related health problems.
As of 2021, the estimated number of people with diabetes in India was around 77 million. India has one of the top rates of diabetes in the world. This number is expected to continue to rise in the coming years due to issues such as increasing urbanization, sedentary lifestyles, and a growing aging population.
There are two main types of diabetes:
Type 1 Diabetes: It is also identified as insulin-dependent diabetes, this type of diabetes happens when the body is incapable to produce insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. It is usually diagnosed in juvenile or early adulthood and requires daily insulin doses or the use of an insulin pump.
Type 2 Diabetes: This is a highly widespread form of diabetes and appears when the body develops resistance to insulin or is incapable of producing sufficient insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. It typically develops in adulthood and can often be managed through lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, and medication.
Others: There are also other, less common types of diabetes, such as gestational diabetes (occurs during pregnancy), maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY), and latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA).
Type 2 diabetes is a recurring condition in which the body is unable to effectively utilize insulin (a vital hormone produced by the pancreas to regulate the sugar levels in the blood). This results in high levels of glucose in the blood, which can cause a range of health problems if left uncontrolled.
Type 2 diabetes typically develops in adulthood, although it is occurring more commonly in children and adolescents nowadays and is often linked to lifestyle factors such as being overweight, having a sedentary lifestyle, and following an unhealthy diet.
Managing Diabetes
Diabetes can be controlled through lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet, being physically active, and losing weight, through medications, such as oral hypoglycemic agents and insulin injections. Effective management of type 2 diabetes can help prevent or delay the development of related health problems, such as nerve damage, heart disease, and kidney disease.
Research centers and Institutes: International
There are many diabetes research centers across the world dedicated to improving our understanding of this condition and developing new treatments and therapies. Some well-known diabetes research centers include:
- Joslin Diabetes Center - Located in Boston, Massachusetts, this is one of the world's leading diabetes research institutions and is known for its innovative approaches to diabetes care, research, and education.
- Helmholtz Center Munich - This is one of the largest medical research centers in Europe, with a focus on diabetes research, including the development of new treatments, therapies, and technologies.
- University of Pittsburgh Diabetes Institute - This institute is dedicated to the advancement of diabetes research, with a focus on both basic and clinical research.
- Diabetes Research Institute (DRI) - Located in Miami, Florida, this institute is dedicated to finding a cure for diabetes through cutting-edge research and innovative treatments.
- King's College London Diabetes & Nutritional Sciences Division - This division is part of one of the largest and most comprehensive medical schools in Europe, with a focus on diabetes research, including the development of new treatments, therapies, and technologies.
Research centers and Institutes: India
Several diabetes research centers in India are dedicated to improving our understanding of this condition and developing new treatments and therapies. Some well-known diabetes research centers in India include:
- Madras Diabetes Research Foundation (MDRF) - Located in Chennai, this is one of the largest diabetes research centers in India, focusing on basic and clinical research, as well as diabetes education and care.
- Diabetic Association of India (DAI) - This is a national organization dedicated to improving the lives of people with diabetes in India, with a focus on diabetes research, education, and care.
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) - This is one of India's leading medical research institutions, with a focus on diabetes research, including the development of new treatments, therapies, and technologies.
- Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) - This is India's leading medical research organization, with a focus on diabetes research, including the development of new treatments, therapies, and technologies.
- National Institute of Nutrition (NIN) - This is one of India's leading nutrition research institutions, focusing on diabetes research, including the impact of diet and nutrition on the development and management of diabetes.
There are other several diabetes research centers in India working to advance our understanding of this condition and find new ways to treat and manage it.
Symptoms of diabetes
The symptoms of diabetes can vary, but some of the most common signs include:
- Increased thirst and frequent urination: As the body tries to get rid of excess glucose, people with diabetes may experience an increase in thirst and may need to urinate more often.
- Fatigue: High blood sugar levels can lead to fatigue and lack of energy.
- Blurred vision: High sugar levels in the body can cause fluid to build up in the eyes, leading to blurred vision.
- Slow healing of cuts and bruises: High blood sugar levels can affect the ability of the body to heal properly.
- Tingling, itchiness, or numbness in the hands and feet: It can damage nerves, leading to tingling or numbness in the extremities.
- Unexpected weight loss: Despite eating more, people with uncontrolled diabetes may lose weight as their body breaks down muscle and fat for energy.
- Frequent infections: It can weaken the body’s immune system, leading to difficulty in fighting infections.
These are some of the most common symptoms of diabetes, but it is important to note that some people may not experience any symptoms at all, especially in the early stages of the disease.
Role of Insulin: Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates glucose (sugar) levels in the blood. It helps the body to use glucose for energy or store it for later use. In people with diabetes, either the pancreas doesn't produce enough insulin or the body doesn't react to insulin properly, resulting in high blood sugar levels.
Types of insulin
There are two main types of insulin used for the treatment of diabetes:
- Rapid-acting insulin: This type of insulin works within a few minutes of injection and is used to manage mealtime (postprandial) glucose levels.
- Long-acting insulin: This type of insulin works more slowly, starting to work within several hours of injection and lasting up to 24 hours. It is used to manage overall glucose levels and can be administered once or twice a day.
Insulin therapy is an important part of managing diabetes and is used to help control blood sugar levels. The type, dose, and frequency of insulin used can vary depending on the individual, and a doctor or diabetes specialist can help determine the best treatment plan.
Insulin plays a critical role in regulating the levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. Its main functions are:
Moving glucose from the bloodstream into cells: Insulin acts as a key that unlocks cells, allowing glucose to enter and be used for energy or stored for later use.
Stimulating the liver to store excess glucose as glycogen: When there is too much glucose in the bloodstream, insulin signals the liver to store some of it as glycogen for later use.
Suppressing the release of glucose: Insulin also signals the liver to stop producing and releasing glucose into the bloodstream, helping to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Stimulating the body to store excess calories as fat: When glucose levels are high, insulin signals the body to store excess calories as fat for future use.
Insulin resistance
Insulin resistance is a situation where cells become resistant to the effects of insulin. As a result, the body needs to produce more insulin to keep blood sugar levels under control. Over time, this can lead to a decline in insulin production and an increase in blood sugar levels, leading to the development of type 2 diabetes.
Several factors can contribute to insulin resistance, including:
- Overweight or obesity: Excess body fat, especially in the abdominal area, can contribute to insulin resistance.
- Poor physical activity: A sedentary lifestyle can increase the risk of insulin resistance.
- High blood pressure (HBP): High blood pressure can damage blood vessels and affect insulin sensitivity.
- Abnormal cholesterol levels: High levels of triglycerides and low levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol can increase the risk of insulin resistance.
- Family history: A family history of type 2 diabetes increases the risk of developing insulin resistance.
Insulin resistance can be managed by lifestyle changes such as losing weight, increasing physical activity, and eating a healthy diet. Some medications may also be prescribed to help improve insulin sensitivity and manage blood sugar levels. Working closely with your doctor to develop an individualized management plan for insulin resistance is important.
Medications for Diabetes
Several types of medicines are commonly used to treat type 2 diabetes:
- Metformin: This is a first-line drug for treating type 2 diabetes. It helps to bring down blood sugar levels by reducing the amount of glucose produced by the liver and improving insulin sensitivity.
- Sulfonylureas: These drugs stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin, which helps lower blood sugar levels.
- DPP-4 inhibitors: These drugs help increase the amount of insulin produced by the body and reduce glucose production by the liver.
- GLP-1 receptor agonists: These drugs mimic the action of a hormone called GLP-1, which improves to reduce blood sugar levels by increasing insulin production and reducing glucose production by the liver.
- GLT2 inhibitors: These drugs work by blocking the reabsorption of glucose by the kidneys, which helps to lower blood sugar levels.
- Thiazolidinediones: These drugs improve insulin sensitivity and help lower blood sugar levels.
The type of drug best for you may depend on several factors, including your overall health, other medical conditions, and the severity of your diabetes. In some cases, a combination of drugs may improve blood sugar control.
To manage diabetes, there are several things you can do:
Maintain a healthy diet by following a balanced meal plan and limiting sugary and processed foods.
- Regular physical activity helps regulate blood sugar levels and maintain a healthy weight.
- Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, as prescribed by your doctor.
- Taking medication as prescribed and on time.
- Quitting smoking if you smoke.
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, or counseling.
- Regular visits to your doctor and eye doctor to check for complications.
It is important to remember that every person with diabetes is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. The most effective approach to managing diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical medications tailored to meet your individual needs.
How would you rate this Article ?
Press the number of stars to rate this Magazine.
4.5 Author Points.
Based on 20 Magazines written by this author.
No Magazine Ratings yet




























Please Sign In or Sign Up to leave a Comment.