Test Amit sep
Green hydrogen as sustainable future fuel
Synthesis of methanol and other chemicals: Hydrogen can be used as a reactant in the production of methanol and other chemicals, such as formaldehyde and MTBE.
Hydrogenation reactions: Hydrogen is used in the hydrogenation of unsaturated fats and oils to produce margarine and other products.
Fuel cell production: Hydrogen is used as a fuel in fuel cells, which can generate electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen.
Microelectronics industry: Hydrogen is used in the microelectronics industry as a cleaning agent to remove impurities from silicon wafers.
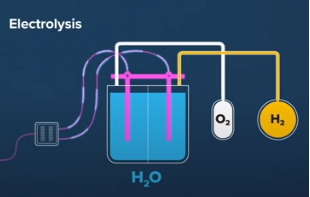
Green hydrogen (GH2) is produced through water electrolysis using renewable energy sources such as solar power and wind. This process does not emit greenhouse gases, unlike the traditional method of producing hydrogen from fossil fuels. Green hydrogen is a key component in the transition to a low-carbon energy system, as it can be used as a clean energy source for transportation, heating, and industrial processes.
Renewable energy refers to energy sources replenished naturally and can be used repeatedly, unlike finite resources like fossil fuels. Examples of renewable energy sources include solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass. Renewable energy is considered a crucial component in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the impacts of climate change. Additionally, renewable energy provides a more sustainable and diversified energy mix, decreasing dependence on fossil fuels and creating new economic opportunities.
A fuel cell is an electrochemical energy conversion device that generates electricity through a chemical reaction between a fuel (usually hydrogen) and an oxidant (usually oxygen). Fuel cells convert chemical energy into electrical energy, with the only byproduct being water and heat. Fuel cells have several advantages over traditional internal combustion engines, including higher energy efficiency, lower emissions, and quiet operation. They are used in various applications, including stationary power generation, material handling, and transportation (especially hydrogen fuel cell vehicles). Fuel cells are also being explored as a potential solution for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting the adoption of clean energy.
Hydrogen production refers to the process of generating hydrogen gas through various means. There are several methods for hydrogen production, including:
Steam methane reforming (SMR): A process that uses natural gas and steam to produce hydrogen.
Electrolysis - a process that splits water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity. This method can be done using renewable energy sources such as wind or solar power to produce "green hydrogen."
Biological methods - the use of microorganisms to produce hydrogen through fermentation.
Coal gasification - a process that converts coal into hydrogen and carbon dioxide.
Natural gas reforming - a process that uses natural gas and high temperatures to produce hydrogen.
The method of hydrogen production depends on various factors, including the cost and availability of energy sources, the desired purity and volume of hydrogen, and environmental considerations. However, green hydrogen production through electrolysis is a key component in transitioning to a low-carbon energy system.
Hydrogen has a wide range of applications, including:
Energy storage - Hydrogen can be stored and transported as a clean and renewable energy source.
Transportation - Hydrogen can be used as fuel for vehicles, such as hydrogen fuel cell cars.
Industrial processes - Hydrogen is used as a raw material in the production of chemicals, fertilizers, and other industrial products.
Power generation - Hydrogen can be burned to produce electricity or used in fuel cells to generate electricity through an electrochemical process.
Space exploration - Hydrogen is used as a rocket fuel and in the cooling systems of satellites and space probes.
Food and beverage industry - Hydrogen is used as a gas in the packaging and preservation of food products.
Welding - Hydrogen is used as a protective gas in welding processes.
Medical applications - Hydrogen is used in the medical field for MRI contrast enhancement and the treatment of certain medical conditions.
Metals processing - Hydrogen is used as a reducing agent in the refining of metals, such as aluminum and titanium.
Hydrogen has a variety of uses in the chemical industry, including:
Refining petroleum: Hydrogen removes impurities such as sulfur from petroleum.
Ammonia production: Hydrogen is a key component in the production of ammonia, which is used as a fertilizer and as a raw material in the manufacture of chemicals.
Synthesis of methanol and other chemicals: Hydrogen can be used as a reactant in the production of methanol and other chemicals, such as formaldehyde and MTBE.
Hydrogenation reactions: Hydrogen is used in the hydrogenation of unsaturated fats and oils to produce margarine and other products.
Fuel cell production: Hydrogen is used as a fuel in fuel cells, which can generate electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen.
Microelectronics industry: Hydrogen is used in the microelectronics industry as a cleaning agent to remove impurities from silicon wafers.
Hydrogen is used in the glass industry for the following purposes:
Reduction of NOx emissions: Hydrogen is used to reduce nitrogen oxides (NOx) emissions during the melting of glass.
Production of specialty glasses: Hydrogen is used in the production of specialty glasses such as heat-resistant and low-expansion glasses.
Decolorization of glass: Hydrogen is used to remove unwanted coloration from glass, such as iron impurities that cause green or brown discoloration.
Refining of raw materials: Hydrogen is used to refine raw materials used in glass production, such as removing impurities from sand and other silica-based materials.
Annealing of glass: Hydrogen is used in the annealing of glass, which is a process of heating and cooling the glass to reduce stress and improve its durability.
The annealing of glass is a thermal treatment process used to reduce internal stress and improve the mechanical properties of glass. During the annealing process, the glass is slowly cooled at a controlled rate to avoid thermal shock, which can cause cracks or other defects. Using hydrogen in the annealing process can provide a controlled and stable atmosphere that helps prevent oxidation and different chemical reactions that can negatively impact the quality of the glass. In addition, hydrogen can help to reduce the risk of defects by reducing the formation of bubbles and other impurities during the cooling process. The result of annealing glass with hydrogen is a stronger, more durable, and higher-quality glass product.
How would you rate this Article ?
Press the number of stars to rate this Magazine.
4.5 Author Points.
Based on 20 Magazines written by this author.
No Magazine Ratings yet




























Please Sign In or Sign Up to leave a Comment.